Custodian & Custodian Account Keeper
The term custodian is not precise and must be distinguished from the role of a central securities depository (CSD). Companies commonly referred to as custodians, such as CACEIS and SGSS, perform several roles governed by different regulatory approvals:
- Credit institutions (supervised by the ACPR) within the meaning of the CRD IV Directive. This status allows them to carry out banking activities such as:
- Accepting deposits and other repayable funds,
- Granting loans,
- Managing payment instruments.
- Investment firms (supervised by the AMF) under the MiFID II Directive, which allows them to provide certain services related to financial instruments, in particular:
- Reception and transmission of orders on behalf of third parties,
- Order execution,
- Custodian account keeping: safekeeping or administration of financial instruments on behalf of third parties (ancillary service).
- Connected to a Central Securities Depository (CSD), which requires authorization under the CSDR (Central Securities Depositories Regulation).
Caceis digital offering:
https://www.caceis.com/fr/espace-demo/olis/
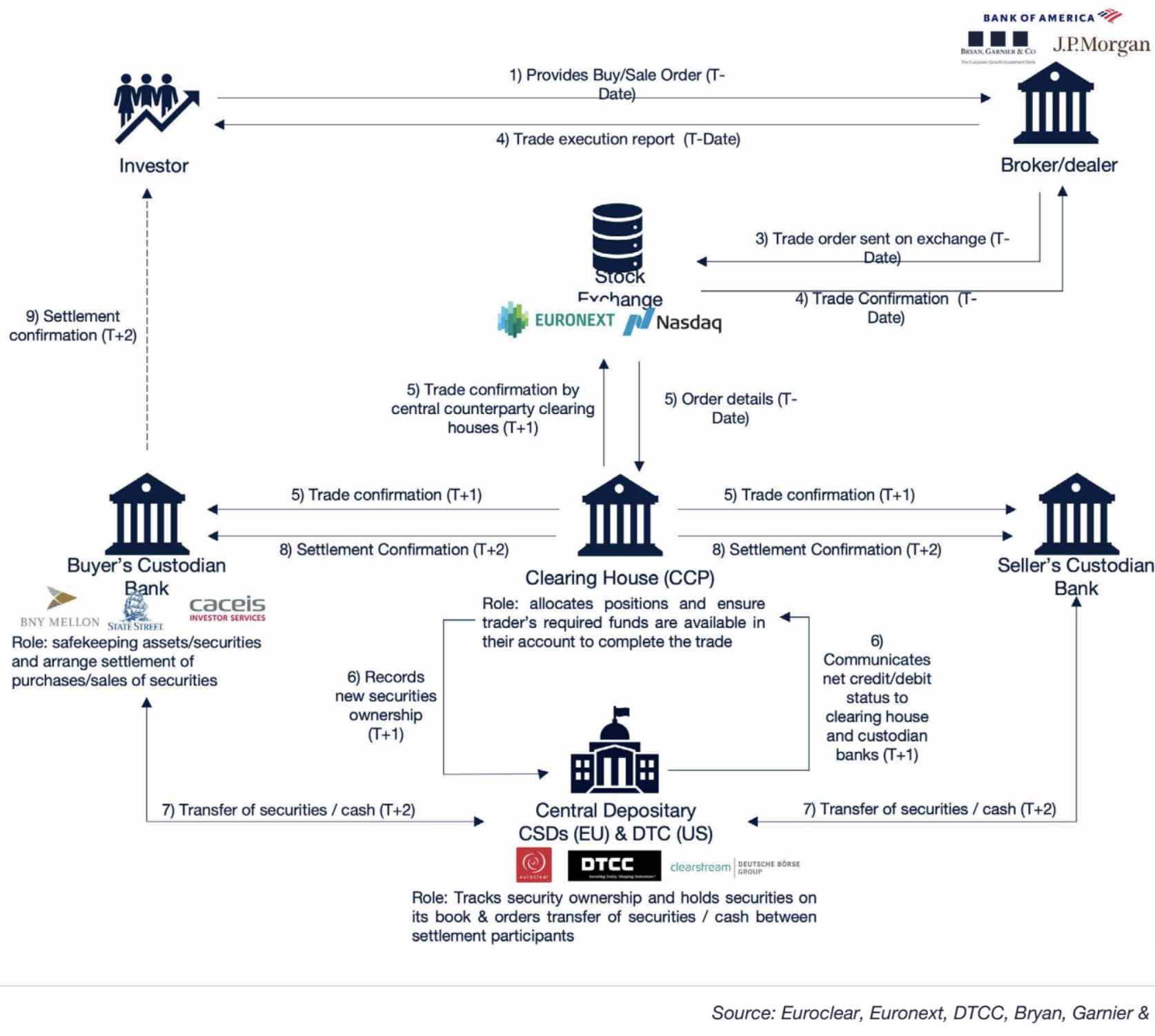
The custodian account keeper is an investment firm authorized by the Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel et de Résolution (ACPR), whose primary role is to ensure the safekeeping of financial instruments in compliance with applicable regulations.
This safekeeping consists, on the one hand, of holding financial instruments in custody on behalf of their owners and, on the other hand, of holding the corresponding assets according to the specific rules applicable to each type of financial instrument.
The custodian account keeper therefore guarantees the positions recorded in clients’ accounts, resulting from buy or sell transactions in financial instruments, or from corporate actions. It handles all types of financial instruments: equities, bonds, collective investment schemes (UCIs), derivatives, etc.
It may hold both domestic and foreign securities.
The custodian account keeper is either a direct participant of a central securities depository or a client of a participant.
The activities of the custodian account keeper are supervised by the Autorité des Marchés Financiers (AMF), which ensures compliance with professional obligations.
Entities authorized or eligible to act as custodian account keepers include banks, financial companies, and investment firms.
Functions Performed
The custodian account keeper is responsible for the administrative and accounting follow-up of transactions carried out on financial markets by its clients. It records transactions, formalizes the transfer of ownership, and informs clients about the processing of their operations.
This business mainly covers four functions:
- Settlement / delivery
- Income processing (dividends and interest) and other corporate actions
- Securities and cash accounting for client transactions
- Processing of related taxation
Settlement / Delivery
The custodian account keeper must manage securities and cash flows resulting from transactions initiated by clients (individuals or legal entities, institutional investors, etc.) and reconcile transactions with counterparties through the various market infrastructures. This function includes the following actions:
- Checking securities and cash availability,
- Initiating settlement and delivery instructions in the various information systems,
- Posting transactions to the accounts,
- Producing reporting related to transactions.
Corporate Actions
The processing of events occurring during the life of a security includes:
- Verifying the announcement of a corporate action and communicating it to clients,
- Handling client instructions, verifying them, and transmitting them to the intermediaries processing the action,
- Posting the transaction to clients’ accounts.
Examples:
- Payment of dividends and interest,
- Redemptions for the securities concerned.
Securities and Cash Accounting
Any transaction recorded by the custodian account keeper modifies the securities and cash accounting position of the relevant client.
Securities accounting follows a specific standardized chart of accounts, similar to cash accounting, notably based on double-entry bookkeeping, with the account structure defined by the AMF.
The custodian account keeper regularly reconciles the positions recorded in its books with those recorded in the books of its correspondents and of the central securities depository.
Tax Processing
Each financial transaction includes a tax component that requires:
- Analysis and application of the relevant tax treatment,
- Examples: withholding tax, exemptions, tax reclaim, etc.,
- Where applicable, preparation of tax documentation for the client,
- Reporting of income and capital gains received by the client to the relevant tax authorities and to the client.

